In thermal cutting, different types of shielding and cutting gases are used
Gases used in thermal cutting account for a part of the total cutting cost. How the gas is delivered (single tube, 12-pack, tank or self-produced) greatly affects the gas price and thus the final production cost.
In addition to creating the cut, the gases also help protect the cutting process from contamination.
By choosing cutting gases with higher purity, which however cost more, one can usually increase the cutting speeds.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Gases for Laser cutting
For laser cutting, two different types of gases are affected. Laser gases required to create the laser beam (CO2 laser) as well as cutting gases that contribute directly to the cutting process.
Laser gases
- The CO2 resonator is a so-called gas laser which means that the beam is created in a space filled with gas ...
- Carbon dioxide
- nitrogen
- Helium
- Nd: The YAG resonator and the Fiber resonator need no laser gases but are so-called solid state lasers where the laser beam is created in a solid medium
Cutting gases
In addition to contributing to the cutting process itself, the cutting gases also aim to keep the laser beam's path free of contamination and protect the lens from splashes.
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen, which is inert, thus does not react with the environment.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Gases for Plasma Cutting
For example, Plasma Cutting 2D uses gases to perform and support the cutting process.
Plasma gases
Plasma gas is the gas that is ionized by tensioning between the anode (nozzle) cathode (workpiece) and thus creating an extremely high temperature plasma that melts / burns the material.
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Argon-based gas
Shielding gases
By adding a protective gas that encloses the plasma gas, the jet is protected against pollution.
- Air
- Carbon dioxide
- nitrogen
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Gases for gas cutting
For example, Gas Cutting 2D uses gases to perform and support the cutting process itself.
Burning gas
The burning gas is the gas that preheats the workpiece up to a temperature near the melting point.
- Propane
- Acetylene
- propylene
Cutting gas
The gas supplied to ignite the heated material creating the cut.
- Oxygen
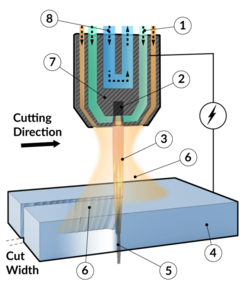
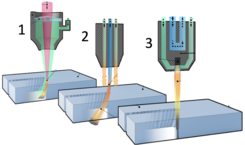
LASER
Plasma cutting 2D
Thermal cutting